Built in 1977, the telescope was originally designed to test polarization multiplexing of signals to geosyncronous satellites at K band and for radio astronomy up to 300 GHz. As a result, it features many of the CMB measurement requirements: A complete description of the antenna is given in Chu et al.(1978).
The main reflector is a 7-meter diameter section of a paraboloid with a focal length of 6.5659 m. It is offset such that its bottom is 1.2074 m above the reflector axis. The surface accuracy of the mirror is ~ 50 10-6 m , much less than the Ku-band wavelength.
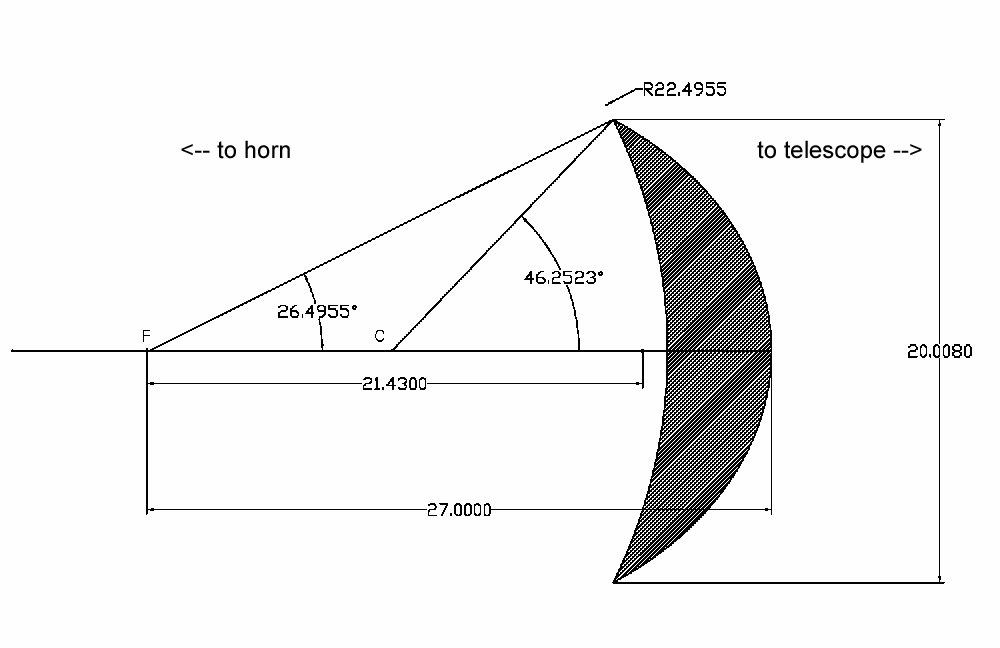
The subreflector is a 1.2 m x 1.8 m oval section of a hyperboloid offset 8.258 cm above its axis. It has focal lengths of 0.8697 m and 5.2262 m providing a magnification ratio of the equivalent system equal to 6.01.
The central ray from the feedhorn to the subreflector makes an angle of 6.828 degrees with the axis, projecting a 5.06 deg half-angle illumination cone. The main reflector is subtended by a circular cone of 26.75 deg half angle, and the axis of this cone makes an offset angle of 37.26 deg with the axis of the main reflector. The geometry results in a blocking of 4.4 cm of the main reflector by the subreflector and an expected contribution to the crosspolarization level of -56 dB in the main beam. During 2001-2005, the telescope has been used by the CAPMAP team to detect CMB polarization at 36- 45 GHz and 84-100 GHz. Large amounts of work have been invested to repair and upgrade the various mechanical, electrical and software system (see The CAPMAP Instrument and its first Season). The control system is described by Denis Barkats in his PhD thesis.